Unique phenanthrenequinone imidazole-based fluorescent materials with aggregation-induced or two-photon emission†
Abstract
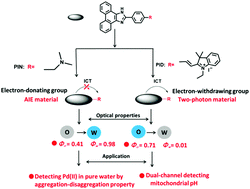
Very recently, aggregation-induced emission (AIE) and two-photon (TP) emission materials have attracted great attention owing to their widespread applications. Herein, interestingly, we described a unique single fluorophore core with different substituents that can show either outstanding AIE or TP fluorescence properties. The introduction of an electron donating unit such as a tertiary amine group on the phenanthrenequinone imidazole core afforded a novel AIE-based fluorescent material PIN. The optical studies of PIN revealed that appropriate structural modifications on the phenanthrenequinone imidazole core could result in AIE character. On the other hand, modification of an electron-withdrawing moiety such as an indolium moiety on the same phenanthrenequinone imidazole-core provided a new material PID, which exhibited favorable TP emission, indicating that phenanthrenequinone imidazole derivatives could be exploited as TP materials. Furthermore, we have demonstrated that the novel AIE or TP materials constructed herein can be successfully applied for sensing targets of interest in aqueous and biological settings owing to their highly desirable emission profiles. The intriguing finding that careful modification of the phenanthrenequinone imidazole scaffold could afford excellent AIE or TP materials may open a new avenue to engineer robust materials with diverse properties based on a versatile core for various applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...