Controlled protein adsorption and delivery of thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanogels†
Abstract
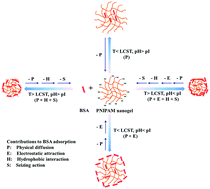
The controlled protein adsorption and delivery of thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) nanogels were investigated under different temperatures, pH values and ionic strengths by using bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a model protein. The BSA adsorption in deionized water was due to one or several of four contributions, i.e. the electrostatic attraction between BSA and nanogels, the seizing action of nanogels to BSA, the hydrophobic interaction between BSA and nanogels, and the physical diffusion of BSA, depending on the temperature and pH value. At 37 °C and pH 4.0, the largest BSA adsorption of 23.5 μg mg−1 was achieved by the above four contributions following electrostatic attraction (48%) > seizing action (21%) > hydrophobic interaction (16%) > physical diffusion (15%). The BSA adsorption in different sodium chloride solutions exhibited a maximum of 17.2 μg mg−1 at 0.03 M, which was influenced by the charge shielding of Na+ ions, salting out of BSA and nanogel aggregation. Most adsorbed BSA molecules were distributed on the nanogel surface except a few standing in the nanogel interior. The adsorbed BSA could be controllably delivered by tailoring the temperature and pH value, and with the aid of sodium dodecyl sulfate. The conformation of BSA adsorbed in hydrochloric acid solution (pH 4.0) significantly changed due to the acid environment and the electrostatic attraction between BSA and nanogels, but it could be completely recovered when BSA was delivered in deionized water or physiological saline. This work is instructive to design the controllable adsorption and delivery of proteins by using PNIPAM-based hydrogels as carriers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...