How a grafting anchor tailors the cellular uptake and in vivo fate of dendronized iron oxide nanoparticles†
Abstract
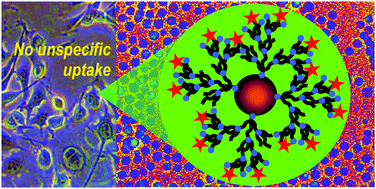
Superparamagnetic spherical iron oxide nanoparticles of 10 nm diameter have been synthesized by thermal decomposition and grafted through a direct ligand exchange protocol with two dendrons bearing respectively a monophosphonic anchor (D2) or a biphosphonic tweezer (D2-2P) at their focal point. Physico-chemical characterization techniques such as dynamic light scattering (DLS), zeta potential, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometry were used to assess their composition, colloidal stability and magnetic properties. High-resolution magic angle spinning (HR-MAS) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy studies have been conducted to understand the organic shell composition and to determine both the grafting rate of the dendrons onto the nanoparticle surface and the influence of the remaining oleic acid originating from the synthesis protocol on the cellular uptake. Both dendronized IONPs showed moderate in vitro toxicity (MTT and LDH tests) in human cancer and primary cell lines. Furthermore, in vivo MRI studies showed high contrast enhancement as well as renal and hepatobiliary excretions and highlighted the influence of the grafting anchor (mono- versus bi-phosphonate) on the in vivo fate of dendronized magnetic iron oxides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...