Bioresponsive controlled glucose release from TiO2 nanotube arrays: a simple and portable biosensing system for cocaine with a glucometer readout
Abstract
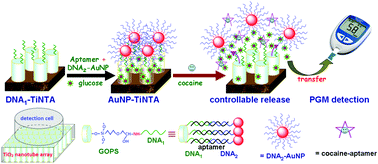
Herein, we design a simple and portable biosensing platform for the quantitative detection of cocaine based on target-triggered glucose release from a TiO2 nanotube array (TiNTA) with a glucometer readout. Initially, single-stranded DNA1 and DNA2 were covalently conjugated to the TiNTA and gold nanoparticle (AuNP), respectively. In the presence of cocaine aptamer and glucose, the immobilized DNA1 on the TiNTA and the labeled DNA2 on the AuNP simultaneously hybridized with the adjacent area of the aptamer, and gated the glucose molecules in the nanotubes. Upon the introduction of cocaine, the aptamer specifically reacted with an analyte to form the target–aptamer complex, thus resulting in the dissociation of DNA1–TiNTA and DNA2–AuNP to release glucose molecules from the nanotubes. The as-released glucose molecules could be determined on a personal glucometer (PGM). The experimental results revealed that the PGM signal increased with increasing cocaine concentration, and exhibited a wide linear range of 10–600 nM with a detection limit of 5.2 nM. Intra- and inter-assay relative standard deviations with identical batches were less than 9.3% and 12.7%, respectively. The specificity, reproducibility, and stability of our strategy were acceptable. Importantly, this concept offers promise for a rapid, simple, low-cost, and user-friendly analysis of small-molecular cocaine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...