Construction of blood compatible lysine-immobilized chitin/carbon nanotube microspheres and potential applications for blood purified therapy†
Abstract
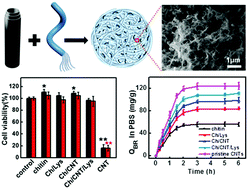
Excess bilirubin often evokes hepatobiliary system dysfunction. In the present work, we developed an efficient, safe and blood compatible adsorbent for bilirubin removal from human blood. In view of the highly effective adsorption of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) on bilirubin but with many side effects, and good biocompatibility of chitin but with low efficiency for bilirubin removal, new chitin/carbon nanotube (Ch/CNT) nanofibrous microspheres were constructed from chitin solution in NaOH/urea aqueous system by blending with CNTs. The results of AFM, SEM, and TEM demonstrated that the CNTs were dispersed well in the chitin matrix, and the chitin nanofibers intertwined with CNTs to form hybrid chitin/CNT nanofibers and then weaved into a 3D interconnected network architecture. Moreover, lysine (Lys), a highly specific ligand for bilirubin, was immobilized tightly to the hybrid microspheres to obtain Ch/CNT/Lys. The resultant microspheres possessed large surface area and hierarchical pores including mesopores and micropores, which could allow bilirubin to enter easily and store, leading to highly efficient adsorption. The Ch/CNT/Lys microspheres exhibited excellent bilirubin adsorption property (107.2 mg g−1) and efficient bilirubin clearance rate from real hyperbilirubinemia plasma competing with protein, as well as good cell affinity and blood compatibility, as a result of the combination of the high adsorption of CNTs and inherent biocompatibility of chitin and lysine. Therefore, an effective strategy to develop a novel biocompatible and blood compatible bilirubin adsorbent is provided, showing potential applications for hemoperfusion in blood purified therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...