A degradable nanogel drug carrier crosslinked with three-oligonucleotide hybrids for two-way drug release in mild and high hyperthermia treatment
Abstract
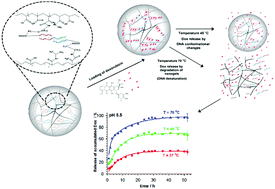
Three-segment oligonucleotide hybrids were introduced as crosslinkers to a PNIPA–AAc nanonetwork. The obtained nanogels could be specifically transformed and degraded. The specific architecture of the presented carrier aims at achieving effective cancer treatment with reduced side toxicity. As a result, compared to the gels with regular crosslinkers, the drug release could be independently realized by (a) changing the structure of the gel net and conformation of DNA hybrids in an oscillating way and (b) degradation of DNA crosslinkers by denaturation. The hydrodynamic diameter and zeta potential of the nanogels were examined as a function of T and pH. The presence of a DNA helix in the nanogels led to a substantial increase, of nearly three times, in the storing efficiency of the selected anticancer drug compared to the nanogels with regular crosslinkers. Moreover, the nanogels allowed 98% drug release efficiency at high hyperthermic and 70% at mild hyperthermic conditions. The effectiveness of cytotoxicity of insulinoma cells was better compared to free doxorubicin. Since in the proposed approach, in addition to the drug, the third DNA strand can be also liberated, this opens new possibilities in development of gene therapies. This novel biocompatible carrier exhibits enhanced drug loading, possesses tunable and degradable properties under hyperthermic conditions and offers controlled release of the drug.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...