Controlling integrin-based adhesion to a degradable electrospun fibre scaffold via SI-ATRP†
Abstract
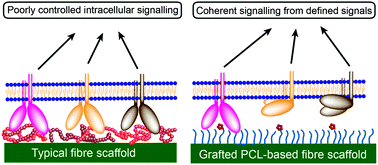
While polycaprolactone (PCL) and similar polyesters are commonly used as degradable scaffold materials in tissue engineering and related applications, non-specific adsorption of environmental proteins typically precludes any control over the signalling pathways that are activated during cell adhesion to these materials. Here we describe the preparation of PCL-based fibres that facilitate cell adhesion through well-defined pathways while preventing adhesion via adsorbed proteins. Surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerisation (SI-ATRP) was used to graft a protein-resistant polymer brush coating from the surface of fibres, which had been electrospun from a brominated PCL macroinitiator. This coating also provided alkyne functional groups for the attachment of specific signalling molecules via the copper-mediated azide–alkyne click reaction; in this case, a cyclic RGD peptide with high affinity for αvβ3 integrins. Mesenchymal stem cells were shown to attach to the fibres via the peptide, but did not attach in its absence, nor when blocked with soluble peptide, demonstrating the effective control of cell adhesion pathways.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...