Fabrication of polymeric biomaterials: a strategy for tissue engineering and medical devices
Abstract
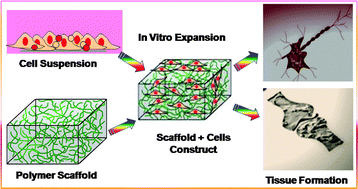
Polymeric biomaterials have a significant impact in today's health care technology. Polymer hydrogels were the first experimentally designed biomaterials for human use. In this article the design, synthesis and properties of hydrogels, derived from synthetic and natural polymers, and their use as biomaterials in tissue engineering are reviewed. The stimuli-responsive hydrogels with controlled degradability and examples of suitable methods for designing such biomaterials, using multidisciplinary approaches from traditional polymer chemistry, materials engineering to molecular biology, have been discussed. Examples of the fabrication of polymer-based biomaterials, utilized for various cell type manipulations for tissue re-generation are also elaborated. Since a highly porous three-dimensional scaffold is crucially important in the cellular process, for tissue engineering, recent advances in the effective methods of scaffold fabrication are described. Additionally, the incorporation of factor molecules for the enhancement of tissue formation and their controlled release is also elucidated in this article. Finally, the future challenges in the efficient fabrication of effective polymeric biomaterials for tissue regeneration and medical device applications are discussed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Highlighting materials research in the UK for biology and medicine

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...