A novel peptide-based fluorescent chemosensor for measuring zinc ions using different excitation wavelengths and application in live cell imaging†
Abstract
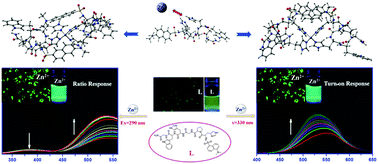
A novel peptide-based fluorescent chemosensor L (Dansyl-His-Pro-Gly-His-Trp-Gly-NH2) containing both tryptophan and a dansyl fluorophore has been designed and synthesized by solid phase peptide synthesis with Fmoc chemistry, which can serve as a promising analytical tool for detecting Zn2+ in 100% aqueous solution and living cells. The fluorescence emission intensity of L can be significantly enhanced in the presence of Zn2+via two pathways, one is the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) effect by ratiometric response at an excitation wavelength of 290 nm, while the other is the chelation enhanced fluorescence (CHEF) effect by turn-on response at an excitation wavelength of 330 nm. The binding stoichiometry and affinity, interference test, pH sensitivity, and cytotoxicity of the chemosensor L to Zn2+ were also investigated. The results show that L performs so well in achieving multiple response detection using different excitation wavelengths that it can suffice the requirement of intracellular biosensing. Interestingly, two types of combination modes may exist in the coordination between L and Zn2+ in aqueous solution. Moreover, L exhibits excellent cell permeation and low biotoxicity with the limit of detection (LOD) for Zn2+ about 97 nM, implying that L can be used as a highly selective and sensitive peptide fluorescent chemosensor in biological systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...