Development of injectable citrate-based bioadhesive bone implants†
Abstract
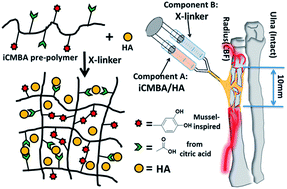
Injectable bone implants have been widely used in bone tissue repairs, including the treatment of comminuted bone fractures (CBF). However, most injectable bone implants are not suitable for the treatment of CBF because of their weak tissue adhesion strengths and minimal osteoinduction. Citrate has been recently reported to promote bone formation through enhanced bioceramic integration and osteoinductivity. Herein, a novel injectable citrate-based mussel-inspired bioadhesive hydroxyapatite (iCMBA/HA) bone substitute was developed for CBF treatment. Note that iCMBA/HA can be set within 2–4 minutes and the as-prepared (wet) iCMBA/HA possesses low swelling ratios, compressive mechanical strengths of up to 3.2 ± 0.27 MPa, complete degradation in 30 days, suitable biocompatibility, and osteoinductivity. This is also the first time that citrate supplementation in osteogenic medium and citrate released from iCMBA/HA degradation has been demonstrated to promote the mineralization of osteoblastic differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). In vivo evaluation of iCMBA/HA in a rabbit comminuted radial fracture model showed significantly increased bone formation with markedly enhanced three-point bending strength compared to the negative control. Neovascularization and bone ingrowth, as well as highly organized bone formation, were also observed, showing the potential of iCMBA/HA in treating CBF.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...