Undecylprodigiosin conjugated monodisperse gold nanoparticles efficiently cause apoptosis in colon cancer cells in vitro†
Abstract
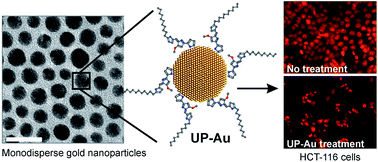
Bacterial pigment undecylprodigiosin (UP) was produced using Streptomyces sp. JS520 and conjugated to monodisperse gold nanoparticles (UP–Au). Both UP and UP–Au showed cytocidal activity towards melanoma (A375), lung carcinoma (A549), breast cancer (MCF-7) and colon cancer (HCT-116) cells, inducing apoptosis with IC50 values ranging from 0.4 to 4 μg ml−1. Unconjugated UP had a tendency to lose its activity over time and to change biophysical characteristics over pH. The loss of the pigment potency was overcome by conjugation with gold nanoparticles. UP–Au exhibited high stability over pH 3.8 to 7.4 and its activity remained unaffected in time. Nano-packing changed the mechanism of UP toxicity by converting the intracellular signals from a mitochondrial dependent to a mitochondrial independent apoptotic process. The availability of nonpyrogenic UP in high amounts, together with specific anticancer activity and improved stability in the complex with gold nanoparticles, presents a novel platform for further development of UP–Au complexes as an anticancer drug suitable for clinical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...