Development of an efficient immobilization matrix based on a conducting polymer and functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes: synthesis and its application to ethanol biosensors
Abstract
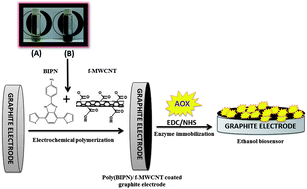
Material modification is one of the hot topics recently. Hereby a novel functional monomer, 2-(4-nitrophenyl)-4,7-di(thiophen-2-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole (BIPN), was synthesized for matrix generation through electrochemical polymerization. Its conducting polymer was successfully used for the biolayer construction in the biosensor preparation. The electrochemical and morphological properties were improved by the introduction of carboxylic acid functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes (f-MWCNTs). Carboxylic acid functionalization of MWCNTs was carried out via acid treatment. The electrode surface was modified with the polymer and f-MWCNTs during electropolymerization to achieve a perfect immobilization matrix for alcohol oxidase. In order to prepare a new alcohol biosensor, alcohol oxidase (AOx) was immobilized onto the modified electrode. The modified electrode was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray photoelectron microscopy (XPS) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy techniques. Electrochemical responses of the enzyme electrodes were monitored at −0.7 V vs. Ag reference electrode by monitoring oxygen consumption in the presence of ethanol. Kinetic parameters, operational and storage stabilities were investigated. KappM, Imax, LOD and sensitivity were calculated as 16.946 mM, 3.31 μA, 0.806 mM and 476 μA mM−1 cm−2, respectively. Finally, this biosensor was applied to estimate the alcohol content in various beverages successfully.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...