A P2-type Na0.44Mn0.6Ni0.3Cu0.1O2 cathode material with high energy density for sodium-ion batteries†
Abstract
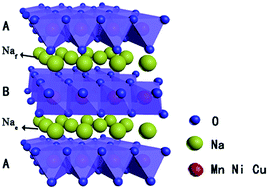
The lack of high-performance cathode materials is a great challenge for the development of large-scale energy storage sodium ion batteries. Here, a new resource-rich P2-type Na0.44Mn0.6Ni0.4−xCuxO2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.3) sodium-ion battery (NIBs) cathode material was designed and synthesized by a sol–gel method. Na ions occupy the Naf sites and the Nae sites in a proportion of 1 : 1, which maintains the high symmetry and stability of the P2-type structure. The charging/discharging tests show that Na0.44Mn0.6Ni0.3Cu0.1O2 has a high initial capacity of 149 mA h g−1 and 80% capacity retention after 50 cycles at 0.1C, showing a high energy density of 469 W h kg−1. The addition of inactive copper enhances the lattice spacing, obviously reducing the irreversible reaction resistance (Rf) during the intercalation and deintercalation of Na+, thereby reducing the internal resistance of the battery and improving the cycle performance. In order to maintain the P2-type structure, the voltage is controlled at 1.5–4.0 V during charging and discharging, which inhibits the phase transition of P2-O2, leading to the improvement of cycling performance. Therefore, the Cu-substituted Na0.44Mn0.6Ni0.3Cu0.1O2 possibly serves as a promising high capacity, high energy density and stable cathode for sodium ion battery applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...