Synergistic effects of a TiNb2O7–reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite electrocatalyst for high-performance all-vanadium redox flow batteries†
Abstract
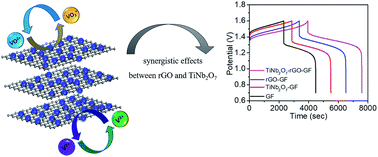
In this study, a simple, low-cost, and powerful titanium niobium oxide–reduced graphene oxide (TiNb2O7–rGO) nanocomposite electrocatalyst was synthesized through dispersion and blending in aqueous solution followed by freeze-drying and annealing for all-vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs). The TiNb2O7 nanoparticles are uniformly anchored between the rGO sheets; simultaneously, the rGO sheets are separated using TiNb2O7 nanoparticles. The synergistic effects between them prevent the agglomeration of the nanoparticles and restacking of the rGO sheets. The cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy results reveal that among all the prepared samples, the TiNb2O7–rGO nanocomposite electrocatalyst exhibits the most favorable electrocatalytic activity toward VO2+/VO2+ and V3+/V2+ at the positive electrode and the negative electrode, respectively, to facilitate the electrochemical kinetics of the vanadium redox reactions. The corresponding energy efficiency is improved by ∼11.1% and 12.34% at current densities of 80 and 120 mA cm−2, respectively, compared with that of pristine graphite felt. The superior performance of the TiNb2O7–rGO nanocomposite electrode may have been due to the synergistic effects related to the high electronic conductivity of rGO nanosheets and the interfacial properties created within TiNb2O7 and rGO. Furthermore, the charge–discharge stability test demonstrates the outstanding stability of the TiNb2O7–rGO electrode. The TiNb2O7–rGO-based VRFB exhibits negligible activity decay after 200 cycles. The remarkable electrocatalytic activity and mechanical stability are achieved due to the TiNb2O7–rGO nanocomposite being strongly anchored on the graphite felt surface for a substantial time during repetitive cycling.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...