Gradient substitution: an intrinsic strategy towards high performance sodium storage in Prussian blue-based cathodes†
Abstract
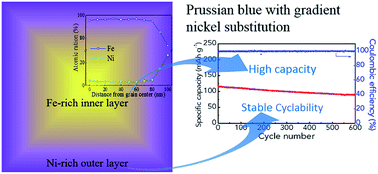
Benefiting from the abundance of sodium, rechargeable sodium ion batteries (SIBs) are preferred over lithium ion batteries (LIBs) in large-scale storage of electrical energy. Low-cost Prussian blue (PB) is a promising cathode because of its ease of synthesis and rigid open framework. Nevertheless, the less activated low spin Fe in FeC6 octahedron lowers the average potential and the overall capacity, while the lattice vacancies and side reactions between low spin Fe and the electrolyte shortens PB's cycling life. Herein, PB with a controllable gradient nickel substitution, which features a high-Ni-content outer layer and low-Ni-content inner layer in a single grain, is demonstrated for high performance sodium storage. The high-Ni-content outer layer efficiently prevents side reactions, ensuring excellent cycling stability, while a small amount of nickel ions in the inner layer efficiently activates the low spin Fe for achieving high capacity. Taking the above synergistic advantages, our gradient-PB exhibits a high reversible capacity of 114 mA h g−1 at 100 mA g−1 and 84 mA h g−1 at 1 A g−1 with very stable cycling for up to 1000 cycles. Gradient substitution in PB analogues provides a novel strategy for exploring high performance PB-based cathodes for SIBs.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...