Experimentation and modelling of nanostructured nickel cermet anodes for submicron SOFCs fuelled indirectly by industrial waste carbon†
Abstract
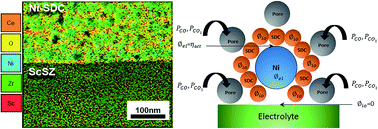
Nickel-Samaria Doped Ceria (Ni-SDC) cermet anodic thin films of about 500 nm were prepared on Scandia Stabilized Zirconia (ScSZ) electrolyte supports via reactive radio frequency (RF) sputtering. Anode deposition was done at room temperature, and the background sputtering gas was a reactive mixture of Ar : O2/80 : 20. The oxide conducting fuel cell configuration was completed by screen printing of lanthanum strontium manganite (LSM/YSZ) cathodes on the other side of the ScSZ supports. High resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) of the cermet anode revealed an arranged nanostructure, with patterned ceria enclosing the nickel molecules in porous media. These highly ordered anodes were tested under (i) H2 and (ii) a product fuel of CO2 electro-reduced via industrial waste carbon (IWC). IWC fuel performance matched the H2 fuel performance in terms of peak power density and longevity, with an added lower fuel cost advantage. HR-TEM and scanning electron microscope (SEM) 2D images were utilized to simulate the reaction kinetics of the nanostructured porous thin film cermet anode. The reported high electrochemical performance was proved to result from the high density of triple-phase boundaries, arranged nanostructure and high contiguity of the special design of the nano-anodes. Experimental and simulation results were coherent with each other, especially for IWC operated SOFCs working at or above 700 °C.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...