Sponge-like quaternary ammonium-based poly(ionic liquid)s for high CO2 capture and efficient cycloaddition under mild conditions†
Abstract
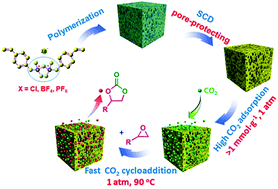
Mesoporous poly(ionic liquid)s (MPILs) are promising candidates for CO2 capture and CO2 conversion; however, no quaternary ammonium-based MPIL has been reported for cycloaddition of CO2 to epoxides. Herein, a series of novel sponge-like crosslinked quaternary ammonium-based MPILs containing rich exposed anions and a large surface area were successfully prepared by free-radical polymerization and subsequent supercritical CO2 drying (SCD). It was discovered that the SCD treatment was vital to form the mesoporous structure of MPILs. These MPILs behaved like a CO2 sponge and facilitated high CO2 adsorption, which accelerated the cycloaddition process. Among these MPILs, poly(N,N′-(methylene)bis(N,N-dimethyl-1-(4-vinylphenyl)methanaminium)chloride) with a halogen anion-enriched skeleton showed the best catalytic performance for CO2 cycloaddition with various epoxides under mild conditions, i.e. 1 atm, 90 °C, solvent-free, metal-free, and additive-free conditions. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations showed that the activation energy was lower for the rate-determining epoxy ring-opening step when the quaternary ammonium monomer was used as compared to the case when the imidazolium monomer was used, revealing the lower CO2 cycloaddition temperature with the quaternary ammonium-based MPIL. Moreover, the catalyst can be separated easily and reused with high stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...