MOF derived ZnCo2O4 porous hollow spheres functionalized with Ag nanoparticles for a long-cycle and high-capacity lithium ion battery anode†
Abstract
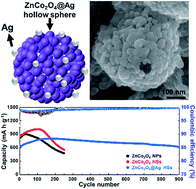
Huge volume expansion during discharge is always a critical problem of high capacity conversion anodes for next generation lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. Although extensive efforts have been devoted to controlling the volume expansion using nanostructuring and surface engineering till now, more simple and facile approaches have to be considered due to the complicated and inefficient synthetic methods. Here, we report a straightforward synthesis of Ag coated ZnCo2O4 porous hollow spheres (ZnCo2O4@Ag HSs): (i) immobilization of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) including Zn and Co metal nodes onto polystyrene sphere templates, (ii) calcination (∼450 °C) for the removal of core polystyrene sphere templates and oxidation of MOFs to produce a mesoporous ZnCo2O4 HSs, and (iii) a subsequent Ag-mirror reaction for 10 min, resulting in the formation of ZnCo2O4@Ag HSs. This porous hollow morphology not only effectively relieves the strain stemming from the volume expansion of transition metals, but also facilitates the efficient electron transport for Li+ diffusion by shortening the Li-ion diffusion path during a lithiation/delithiation process. Moreover, uniformly decorated Ag nanoparticles are beneficial to the formation of a stable solid electrolyte interface (SEI) layer as well as an increased electrical conductivity of ZnCo2O4. The MOF derived porous ZnCo2O4@Ag HSs exhibited remarkably stable cycling performance (a capacity value of 616 mA h g−1 after 900 cycles at a current density of 1 A g−1) and an excellent capacity retention of 80% at a very high current density of 20.0 A g−1.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...