Al2O3 surface coating on LiCoO2 through a facile and scalable wet-chemical method towards high-energy cathode materials withstanding high cutoff voltages†
Abstract
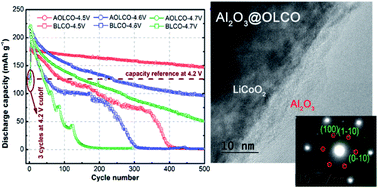
With the increasing demand for high energy density in portable-device Li-ion batteries (LIBs), efforts are devoted to increase and stabilize the capacity of LiCoO2 at high operation voltages. Herein, we report a low-cost and eco-friendly wet-chemical method to coat Al2O3 on LiCoO2, using only aluminium sulphate and water as source materials. A nanoscale oxide layer is coated on the surface of LiCoO2 particles through hydrogen-bonding assisted adsorption of the hydrolysed Al(OH)3 nanoparticles. The as-proposed Al2O3-coating provides excellent physico-chemical protection and kinetically-favourable interfaces for the LiCoO2 electrode, resulting in remarkable improvements of the electrode's cycling stability and rate capability when tested at high cutoff voltages up to 4.7 V (vs. Li/Li+). The synergetic effects of the oxide coating, e.g. alleviated electrolyte decomposition and reduced generation of irreversible solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) constituents (LiF/Li2CO3 and organics), are attributed to the improvements. At the cutoff voltage of 4.5 V, the modified LiCoO2 electrode in this work exhibits excellent cycling stability (147 mA h g−1, 82.6% retention after 500 cycles at 1C) and competitive rate capability (130 mA h g−1 at 10C), which are some of the best results reported so far. The outstanding high-voltage electrode performance and the simple and scalable coating approach show great promise of LiCoO2 cathodes in future high-energy and high-power LIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...