Performance and DRT analysis of P-SOFCs fabricated using new phase inversion combined tape casting technology†
Abstract
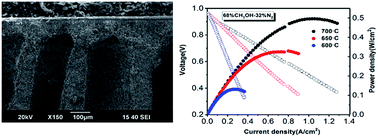
Limited by low volume energy density, high flammability and wide explosive limit of hydrogen fuel, SOFCs directly adopting hydrogen fuels are being gradually substituted by those using hydrocarbon fuels. Unfortunately, the large molecule of methanol makes it inconvenient to be transported to active sites for efficient anode reactions, and this indeed impedes the electrochemical performance of such hydrocarbon SOFCs. Herein, a new Ni–BaZr0.3Ce0.5Y0.2O3−δ (BZCY) anode substrate, possessing a relatively dense functional layer and large finger-like pores straight to the surfaces, is successfully fabricated using a new phase-inversion combined tape casting technology (PICTC). Fueled with 68% CH3OH–32% N2, the PICTC button cell using BaZr0.3Ce0.5Y0.2O3−δ electrolyte demonstrates a great electrochemical performance with peak power densities of 500 and 330 mW cm−2 measured at 700 and 650 °C, about 40% and 100% higher than those of the traditional cold-pressing cells, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of using liquid hydrocarbon fuels in proton conducting fuel cells (P-SOFCs). In contrast to the general opinion, impedance spectra analysis using distribution of relaxation time (DRT) method suggests that reactions taking place in anode contributed greatly to the total polarization resistances of the fuel cell, which is in good agreement with our observation on the electrochemical performance of the PICTC cell.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...