In situ preparation of a binder-free nano-cotton-like CuO–Cu integrated anode on a current collector by laser ablation oxidation for long cycle life Li-ion batteries†
Abstract
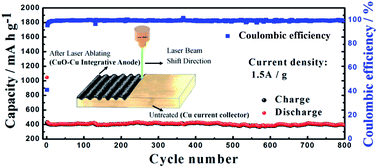
In this paper, we report a unique approach to directly grow nano-scale cotton-like CuO in situ on a Cu current collector using a nano-second laser to ablate it, forming an excellent integrated electrode. This villous nano-cotton CuO is made of micro-scale cotton-like structures, which consist of a huge number of nano-scale particles around 5 nm in diameter. The CuO–Cu integrated anode prepared in 10 minutes by laser ablation exhibits excellent rate performance, coulombic efficiency and a long cycle life. After 800 cycles at 1.5 A g−1, the coulombic efficiency remains higher than 99% and the retention capacity reaches 393.6 mA h g−1. These, to our knowledge, are the highest achieved among currently available CuO integrated anodes. This unique performance is attributed to the villous cotton-like CuO structure, which effectively resists volume expansion and contraction, increases the adhesion of active materials to the current collector, and enhances the conduction of the anode. Laser ablation is a highly efficient and cost-effective approach to prepare integrated oxide-metal anodes for LIBs with a long cycle life. In addition, FexOy–Fe, NixOy–Ni integrated anodes were also prepared for LIBs to verify the wide applicability of this method.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...