Exploring the influence of iron substitution in lithium rich layered oxides Li2Ru1−xFexO3: triggering the anionic redox reaction†
Abstract
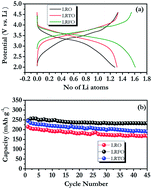
Lithium rich layered materials are an interesting class of materials which exploit both anionic and cationic redox reactions to store energy upwards of 250 mA h g−1. This paper aims to understand the nature of the redox reactions taking place in these compounds. Li2RuO3 was used as the base compound, which is then compared with compounds generated by partially substituting Ru with Ti and Fe respectively. Electrochemical tests indicate that Fe substitution in the sample leads to an improvement in capacity, cycle life and reduction of potential decay. To elucidate the reason for this improvement in operando diffraction experiments were carried out, highlighting the formation of a secondary de-lithiated phase. The distortion of the pristine structure eventually induces frontier orbital reorganization leading to the oxygen redox reaction resulting in extra capacity. Local changes at Fe and Ru ions are recorded using in operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). It was noted that while Ru undergoes a reversible redox reaction, Fe undergoes a significant irreversible change in its coordination environment during cycling. The changes in the coordination environment of oxygen and formation of O2n− type species were probed in situ using soft X-rays.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...