Bismuth-doped La1.75Sr0.25NiO4+δ as a novel cathode material for solid oxide fuel cells†
Abstract
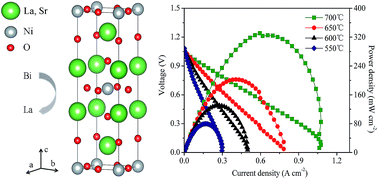
Bismuth has been doped into mixed ionic–electronic conducting La1.75Sr0.25NiO4+δ (LSN) with the 2D K2NiF4-type structure to evaluate its influence on various properties of the host material, which include its potential use as a SOFC cathode. X-ray powder diffraction indicates that LSN retains its tetragonal structure after doping with 5 mol% bismuth to form La1.65Bi0.1Sr0.25NiO4+δ (LSN–Bi). Bismuth doping profoundly lowers (by ∼150 °C) the sintering temperature of LSN. Both LSN and LSN–Bi show excellent compatibility with electrolytes yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) and samaria-doped ceria (SDC) in terms of thermal expansion and chemical reactivity (<900 °C). The electrical conductivity of both materials is metallic like and reaches values of 99.3 S cm−1 and 100.3 S cm−1 at 550 °C for LSN and LSN–Bi, respectively. The data from electrical conductivity relaxation (ECR) measurements demonstrate that the substitution of lanthanum by bismuth enhances the chemical diffusion coefficient (Dchem) and surface exchange coefficient (kchem) by factors of 2–3. The faster kinetics of oxygen transport exhibited by LSN–Bi relative to parent LSN is reflected by a lower polarization resistance of the former when the electrode performance of both materials is compared in symmetric cells. The corresponding values at 700 °C are 4.2 Ω cm2 and 0.61 Ω cm2 for LSN and LSN–Bi, respectively. High peak power densities are achieved (328 mW cm−2 and 131 mW cm−2 at 700 and 600 °C, respectively), when LSN–Bi is incorporated as the cathode in a fuel cell operated with humidified hydrogen as the fuel and air as the cathode gas. The material is considered a promising candidate for further study.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...