Highly active and stable Er0.4Bi1.6O3 decorated La0.76Sr0.19MnO3+δ nanostructured oxygen electrodes for reversible solid oxide cells†
Abstract
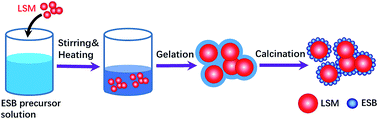
Bismuth based oxides have excellent ionic conductivity and fast oxygen surface kinetics and show promising potential as highly active electrode materials in solid oxide cells (SOCs) such as solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) and solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOECs). However, the low melting temperature and high activity of bismuth based oxides severely limit their wide applications in SOCs. Herein, we successfully synthesized a 40 wt% Er0.4Bi1.6O3 decorated La0.76Sr0.19MnO3+δ (ESB–LSM) electrode via a new gelation method and directly assembled it on a Ni–yttria-stabilized zirconia (Ni–YSZ) cermet supported YSZ electrolyte cell without the conventional high temperature pre-sintering step. ESB decoration substantially enhances the electrocatalytic activity of the LSM electrode for the oxygen reduction/evolution reactions (ORR/OER). A YSZ electrolyte cell with the directly assembled ESB–LSM electrode exhibits a peak power density of 1.62 W cm−2 at 750 °C, significantly higher than 0.48 and 0.88 W cm−2 obtained on cells with a directly assembled pristine LSM and LSM–YSZ composite electrode, respectively. Most importantly the cells with the directly assembled ESB–LSM oxygen electrodes show excellent stability in SOFC, SOEC and reversible SOC operating modes for over 200 h. The present study demonstrates a significant advancement in the development of bismuth based oxide decorated high performance and stable oxygen electrodes for reversible SOCs.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...