Amphiphilic SiO2 hybrid aerogel: an effective absorbent for emulsified wastewater†
Abstract
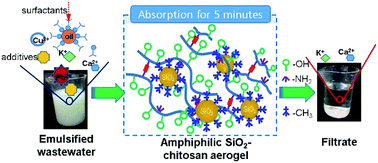
Amphiphilic aerogels based on the SiO2–chitosan composite system with strong purifying capacity to intractable emulsified wastewaters are presented. The hybrid aerogels are realized by integrating the hydrophilic chitosan into an organosilane modified SiO2 nanoframework via sol–gel and ambient drying processes. The uniform hybridization of SiO2 and chitosan nanoparticles (∼3–10 nm) at the nanoscale, small pore size (<12 nm) and high pore volume (1.5–2.0 ml g−1) are demonstrated. The coexistence of multiple functional groups (–OH, –NH2, ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) Si–O–Si(CH2)3NH2, and
Si–O–Si(CH2)3NH2, and ![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) Si(CH3)3) contribute to the amphiphilic properties. The hybrid aerogel powders exhibit good compatibility with and high absorption of both water and oily liquids (up to 6.3 g g−1 for propylene carbonate), together with good regeneration efficiencies (>90% after 10 cycles). An interesting descending trend in the contact angle (from 114.6° to 90.5°) with the measuring time is observed, originating from the nanoporous and amphiphilic surface properties. Rapid (5 minutes) and effective treatment of a high concentration polyacrylic emulsion (chemical oxygen demand (COD): 1 138 000) or on-line machining emulsified wastewater (COD: 471 200) is demonstrated, exhibiting high absorption capacity (5 g g−1) and high purification efficiencies (98.4% and 96%), much better than those with activated carbon. In addition, the simultaneous removal of heavy metal ions (Pb2+ and Cu2+) from the machining emulsified wastewater is observed.
Si(CH3)3) contribute to the amphiphilic properties. The hybrid aerogel powders exhibit good compatibility with and high absorption of both water and oily liquids (up to 6.3 g g−1 for propylene carbonate), together with good regeneration efficiencies (>90% after 10 cycles). An interesting descending trend in the contact angle (from 114.6° to 90.5°) with the measuring time is observed, originating from the nanoporous and amphiphilic surface properties. Rapid (5 minutes) and effective treatment of a high concentration polyacrylic emulsion (chemical oxygen demand (COD): 1 138 000) or on-line machining emulsified wastewater (COD: 471 200) is demonstrated, exhibiting high absorption capacity (5 g g−1) and high purification efficiencies (98.4% and 96%), much better than those with activated carbon. In addition, the simultaneous removal of heavy metal ions (Pb2+ and Cu2+) from the machining emulsified wastewater is observed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...