Interstitial boron-doped anatase TiO2 thin-films on optical fibres: atmospheric pressure-plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition as the key for functional oxide coatings on temperature-sensitive substrates†
Abstract
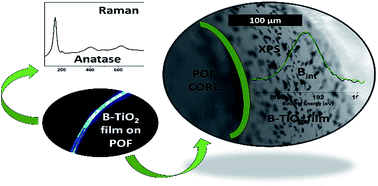
Temperature sensitive poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) optical fibres were coated with boron doped-anatase crystalline TiO2 thin films in a one-step atmospheric pressure-plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition (AP-PECVD) process. Both the undoped and interstitial boron-doped TiO2 thin films showed photoactivity under UV irradiation, with the boron-doped thin films presenting higher photodegradation rates when compared to the undoped samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...