Synthesis of B-doped graphene quantum dots as a metal-free electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction†
Abstract
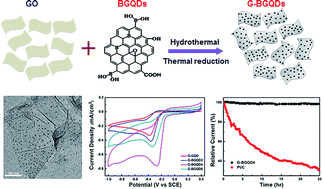
Boron-doped graphene quantum dots (BGQDs) have been synthesized by a one-step, facile and low temperature method through the hydrothermal treatment of glucose as the precursor in the presence of boric acid. The as-obtained BGQDs possess a high B-doping content up to 4.25% of uniform nm-size. Interestingly, the effect of different types of B–C bond species on the ORR catalytic activity has been investigated to clarify the origin of the electrochemical reduction of O2. Further, the composite of the reduced graphene oxide (rGO) and BGQD (G-BGQDs) was also prepared as a metal-free electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). The G-BGQD composites exhibit a significantly enhanced electrocatalytic activity, including a positive onset potential and a high current density with a one step, four-electron pathway toward the ORR, comparable to the commercial Pt/C catalyst. Among various B–C bond structures in BGQDs, the graphite-like BC3 structure is considered to be an important site for the ORR by improving the electric conductivity and electrocatalytic activity of BGQDs, which is also confirmed by a DFT study. In addition, the G-BGQD composites show an outstanding long-term operational stability and high tolerance to the methanol crossover effect, which are comparable to the commercial Pt/C catalyst. These results demonstrate that the synthesized BGQD, as metal-free catalyst materials, may be inexpensive and efficient electrocatalysts for the replacement of Pt-based catalysts toward the ORR and other electrochemical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...