Landscape of DNA-like inorganic metal free double helical semiconductors and potential applications in photocatalytic water splitting
Abstract
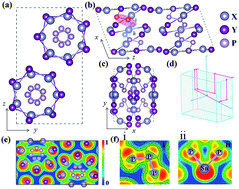
Organic double helical structures such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and poly(tetrafluoroethylene) play important roles in organisms and industry. Enlightened by recent experimental progress, a novel family of DNA-like inorganic metal free structures XYP (X = Si, Ge, Sn; Y = Cl, Br, I) were investigated using first principle calculations. All these structures were identified that as being semiconductors and, in particular, their band gaps corresponded to wavelengths of 419–561 nm, which implies semiconducting absorption in the visible spectra. Partial charge densities indicate an ideal space separation of electrons and holes, which can highly reduce the recombination of carriers in redox reactions. By comparing the band edge positions with the redox potentials of water, it was also found that XYPs are excellent photocatalysts for water splitting. Furthermore, the electron mobility of one-dimensional XYP is estimated to be up to 2164 cm2 V−1 s−1, which is comparable with or even larger than that of other nanomaterials. These systematic studies on DNA-like inorganic semiconductors with applications in photocatalytic water splitting and high speed electronic devices will open a new page in the world of inorganic-DNA nanomaterials.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 Journal of Materials Chemistry A HOT Papers


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...