Facile electrochemical preparation of self-supported porous Ni–Mo alloy microsphere films as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for water splitting†
Abstract
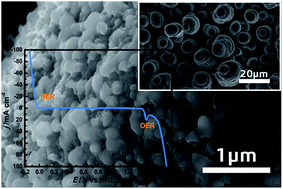
The exploration of low-cost, stable, and robust electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) is urgently needed for developing renewable-energy storage and conversion techniques. In this study, we report a facile one-step electrodeposition route to prepare self-supported porous Ni–Mo alloy microsphere (Ni–Mo MS) films directly grown on copper foils from a deep eutectic solvent, ethaline (mixture of choline chloride and ethylene glycol), as a highly efficient and durable catalyst for both the HER and OER in 1.0 M KOH. The prepared Ni–Mo MS/Cu, as a hydrogen-evolving cathode, shows remarkable catalytic performance toward the HER with a small Tafel slope of 49 mV dec−1 and a low HER overpotential of −63 mV to deliver 20 mA cm−2. Serving as an oxygen-evolving anode, the catalyst also offers excellent OER catalytic activity with a moderate Tafel slope of 108 mV dec−1, and reaches 20 mA cm−2 at an OER overpotential of 335 mV. Utilized as both the cathode and anode in a symmetric two-electrode water electrolysis system, the bifunctional catalyst requires a cell voltage of 1.59 V to reach an overall water splitting current density of 10 mA cm−2 with robust durability, which could be potentially used in water splitting devices for practical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...