Stably dispersed high-temperature Fe3O4/silicone-oil nanofluids for direct solar thermal energy harvesting†
Abstract
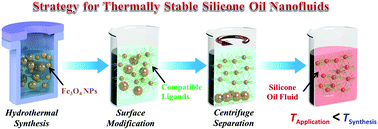
Poor dispersion stability has become one of the major obstacles to the practical application of thermal nanofluids, especially for silicone-oil-based nanofluids that are used at relatively high operating temperatures. Herein, by using Fe3O4 nanofluid as a model system, we report a facile and effective strategy to prepare stably dispersed silicone-oil-based nanofluids that enable high-temperature operation. The strategy involves a series of processes, including controlled high-temperature synthesis of nanoparticles, surface modification of particles, and post-modification particle size partition. The solvothermally synthesized particles not only possess high thermal stability, but also allow for easy surface modification through ligand exchange. Phosphate-terminated polydimethylsiloxane ligands, which simultaneously possess high compatibility with silicone-oil-based fluid and high temperature stability, were used to exchange synthetic ligands and robustly anchor onto the particle surfaces, offering effective screening of the interparticle attraction. After centrifugal removal of the large-sized surface-modified particles, the prepared nanofluids have demonstrated stable dispersion at temperatures slightly lower than the particle synthesis temperature. The stably dispersed Fe3O4/silicone-oil nanofluids have been successfully utilized for consistent volumetric harvesting of solar thermal energy at more than 110 °C.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...