Carbon encapsulated RuO2 nano-dots anchoring on graphene as an electrode for asymmetric supercapacitors with ultralong cycle life in an ionic liquid electrolyte†
Abstract
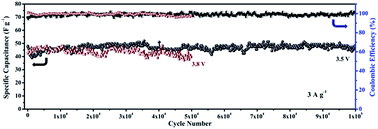
Assembling asymmetric supercapacitors (SCs) combined with ionic liquid (IL) electrolytes is a very efficient strategy to enhance the energy density of SCs. However, the poor cycle stability of pseudocapacitive metal oxides in ILs seriously affects the performance of this class of asymmetric SCs. Improving the structural stability of metal oxides during the charge/discharge process is one of the greatest challenges at present. Herein, RuO2 nano-dots/reduced graphene oxide (RGO) composites are firstly prepared, and an IL-based asymmetric SC is built using the component-optimized composite (20 wt% RuO2/RGO) as the cathode and activated polyaniline-derived carbon nanorods (denoted as APDC) as the anode. It exhibits a high energy density of 108 W h kg−1, but shows poor cycling stability. In order to solve this problem, an ultrathin carbon layer originating from glucose is employed to encapsulate RuO2 nano-dots anchoring on RGO, forming a core/shell structure of RuO2@C. With the protection of the carbon shell, the as-made RuO2@C/RGO//APDC asymmetric SC exhibits superior long-term stability with 98.5% capacitance retention after 100 000 cycles in the IL electrolyte, as well as a high energy density of 103 W h kg−1 with a potential window of 3.8 V. Furthermore, this protection mechanism of the carbon layer is analyzed by electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance experiments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...