Improving the performance of TFC membranes via chelation and surface reaction: applications in water desalination
Abstract
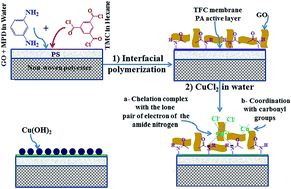
Here we report modification of thin film composite (TFC) membranes via a series of chemical and surface reactions. Initially, the nascent polyamide (PA) active layer was prepared by interfacial polymerization and composited with graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets and then reacted with cupric chloride dihydrate (CuCl2·2H2O). Finally, the composited membrane was treated by a reaction with ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) solution. The chemical modifications of the PA active layer included the formation of a polyamide–copper–graphene oxide complex (PA–Cu2+–GO), whereas, the surface modifications, mineralization, include the formation of copper hydroxide [Cu(OH)2] on the membrane surface through a reaction between the residual CuCl2·2H2O and NH4OH solution. The results of the compositional analysis of mineralized membranes showed that the active layer is fully cross-linked, with Cu2+ chelated with amide nitrogen and coordinated with the carbonyl groups. The membrane performance was evaluated using a cross-flow apparatus at 2000 mg L−1 NaCl solution, 25 °C and a pressure of 15 bar. The mineralized membrane with optimum concentrations of copper chloride and ammonium hydroxide of 0.125 molar and 0.1%, respectively, and a reaction time of 1 minute showed a higher pure water permeability and solute water flux (44.25, 33.77 L m−2 h−1) compared to the pristine TFC membrane (21.36, 20.2 L m−2 h−1) with an excellent salt rejection (≥98.5%). Moreover, the mineralized membranes were found to resist chlorine attack and fouling adsorption more than the non-treated TFC membrane.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...