Fluidized bed electrodes with high carbon loading for water desalination by capacitive deionization†
Abstract
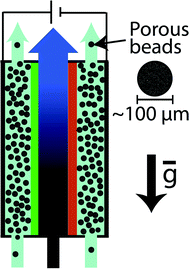
The use of carbon flow electrodes has significantly impacted electrochemical energy storage and capacitive deionization (CDI), but device performance is limited as these electrodes cannot surpass ∼20 wt% carbon while maintaining flowability. We here introduce flowable fluidized bed electrodes which achieve up to 35 wt%, and apply these to water desalination by CDI.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...