Ultra-long electron lifetime induced efficient solar energy storage by an all-vanadium photoelectrochemical storage cell using methanesulfonic acid
Abstract
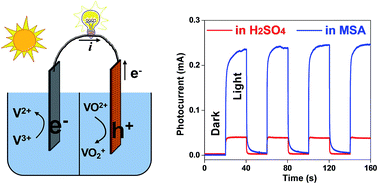
The properties of a supporting electrolyte are critically important to any photo- or electrochemical cells. In this study, we conducted studies on and characterized an all-vanadium photoelectrochemical storage cell (all-V PESC) for highly efficient solar energy storage using methanesulfonic acid (MSA) as a promising supporting electrolyte. Linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) and zero resistance ammetry (ZRA) studies of the all-V PESC show greatly improved photoelectrochemical properties of MSA over conventional H2SO4. To elucidate its heightened performance, the conductivity and reaction kinetics of the system were investigated using four-probe conductivity measurements and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), respectively. The EIS results demonstrate vastly reduced charge transfer resistance and interfacial capacitance at the photoelectrode/electrolyte interface via ultra-long photoelectron lifetime; while the conductivity measurements reveal a comparable bulk ionic conductivity to H2SO4. Cell efficiency tests indicate a nearly 19-fold enhancement in incident photon-to-electron conversion efficiency (IPCE) and a high faradaic efficiency (84.8%) during a continuous 60 h operation using MSA as the supporting electrolyte. Besides, multiple cyclic voltammetry (CV) scans on the electrolyte along with XRD and SEM characterization of the photoelectrode corroborate the exceptional chemical stability of MSA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...