Schottky contact of an artificial polymer semiconductor composed of poly(dimethylsiloxane) and multiwall carbon nanotubes†
Abstract
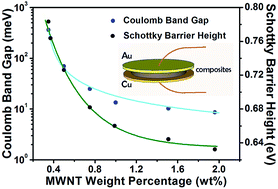
Organic semiconductors have attracted great attention offering an attractive alternative to conventional inorganic semiconductors due to lower costs, simpler synthesis and high flexibility. In this work, we fabricated a flexible organic semiconductor by incorporating multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWNTs) into insulating poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) rubber, and researched the contact properties in the metal/composite junctions. The results reveal that the contact properties depend largely on the work function of the metals and the MWNT loading of the composites. To ascertain the performance variations of the copper/composite junctions characterized by important parameters, Schottky Barrier Heights (SBHs) were measured with various MWNT loading of the composites. The SBH decreased with the increase of the MWNT loading, exceeded 0.783 eV for the 0.35 wt% composite, and shared the same changing trend with the composite Coulomb band gap as a function of the MWNT loading. A quantitative analysis of photo-voltages by the photovoltaic tests was used to verify the reliability of these SBHs. The stability test provides direct evidence that the composites possess good, durable performances at ambient temperature. This work shows that the contact properties in the metal/composite junctions cannot be neglected in the application of the composites in flexible electronics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...