Improved electrochemical performance of the Na3V2(PO4)3 cathode by B-doping of the carbon coating layer for sodium-ion batteries†
Abstract
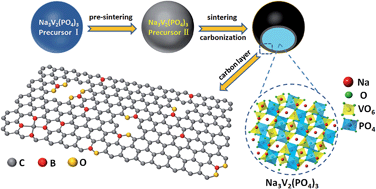
Boron-doped carbon coating is initially used to improve the electrochemical performance of Na3V2(PO4)3 cathode materials of sodium-ion batteries. Based on the precise analysis of Raman spectroscopy, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and X-ray photoemission spectroscopy, it is found that there are four different B-doping species (B4C, BC3, BC2O and BCO2) in various boron-doped carbon coated Na3V2(PO4)3 samples; moreover, different B-doping species in the carbon coated layer have different impacts on the improvement of the electrochemical performance of Na3V2(PO4)3. Compared to lithium-ion batteries, the mechanism of B-doped carbon coating for the improvement of the electrochemical performance in sodium-ion batteries is different. Due to the introduction of the O atom in the carbon coated layer, BC2O and BCO2 significantly increase numerous extrinsic defects and active sites, which could significantly accelerate Na+ transport in the carbon layer. Therefore, it is unexpectedly demonstrated that Na3V2(PO4)3/C + B, which consists of the largest total amount of BC2O + BCO2, exhibits the best electrochemical performance, particularly high-rate performance and cycling stability. As an example, when the discharging rate increases from 0.2 C to 5 C, it delivers 95.8 mA h g−1 to 90.3 mA h g−1 and an amazing capacity retention of 94% is achieved.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...