A strategy for breaking the MOF template to obtain small-sized and highly dispersive polyoxometalate clusters loaded on solid films†
Abstract
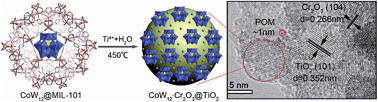
A strategy was developed for the first time to fabricate highly dispersed and small-sized polyoxometalate nanoparticles loaded on a TiO2 film by using MIL-101 to prevent agglomeration, and calcination to break the metal–organic framework, which can result in performance improvement of quantum dot solar cells.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2015 Journal of Materials Chemistry A Hot Papers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...