Highly stretchable dielectric elastomer composites containing high volume fractions of silver nanoparticles†
Abstract
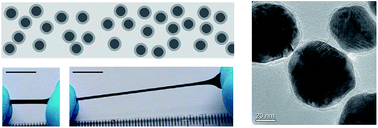
The dielectric permittivity (ε′) of a polymeric material can be significantly increased when blended with conductive fillers at concentrations approaching the percolation threshold. However, reproducible synthesis of such composites is after decades of research still a major challenge and a bottleneck for their application. Difficulties arise in controlling the size and shape of the filler as well as in its homogenous distribution within the composite. These parameters strongly affect the dielectric as well as mechanical properties of the composite. While a substantial amount of literature deals with the influence of conductive fillers on the dielectric properties of composites, little is known about their mechanical properties. It is therefore still an important goal to synthesize materials with simultaneously high ε′ and good mechanical properties. Here, we report the synthesis of dielectric elastomers that combine key properties such as high flexibility and stretchability, high thermal stability, increased ε′, low dielectric loss and conductivity. Such materials were prepared by solution processing using quasi-spherical silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) of a defined size in a polydimethylsiloxane matrix (Mw = 692 kDa). To prevent percolation, the AgNPs were coated with a thin silica shell (<4 nm). To increase their compatibility with the silicone matrix, these core–shell nanoparticles were passivated with a silane reagent. The insulating silica shell around the particles precisely defines the minimum approach distance between the cores as twice the shell thickness. The dielectric properties of the passivated particles (filler) were measured in pellets and found to have an almost frequency independent value of ε′ = 90 and a very low loss factor tan δ = 0.023 at high frequencies. When such particles were used as fillers in a polydimethylsiloxane matrix, composites with low dielectric losses were obtained. A composite containing a 31 vol% filler with ε′ = 21 and tan δ = 0.03 at ∼1 kHz was achieved. At a AgNP volume fraction of 20%, the composite has ε′ = 5.9 at ∼1 kHz, a dielectric strength of 13.4 V μm−1, an elastic modulus as low as 350 kPa at 100% strain, and a strain at break of 800%. Due to the high specific energy density per volume at low electric fields, these composites are attractive materials in applications involving low electric fields.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...