Low temperature synthesized carbon nanotube superstructures with superior CO2 and hydrogen storage capacity†
Abstract
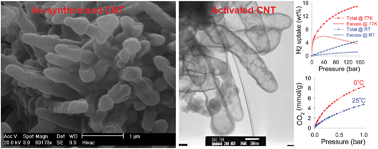
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) may be prepared at a low temperature of 180 °C using carbon tetrachloride as carbon source and ferrocene/Ni as substrate/catalyst. The lowly graphitic CNTs have diameter of 180–300 nm and wall thickness of ca. 25 nm and are arranged into closely networked superstructures with surface area and pore volume of 470 m2 g−1 and 0.39 cm3 g−1, respectively. On activation, the CNT superstructures yield highly porous CNT composites with surface area of 1479–3802 m2 g−1 and pore volume of 0.83–2.98 cm3 g−1. Mild activation generates highly microporous (≥95% microporosity) carbons that retain nanotubular morphology and which exhibit excellent CO2 uptake capacity; up to 4.8 mmol g−1 at 1 bar and 19.5 mmol g−1 at 20 bar and 25 °C, while at 0 °C they store 8.4 mmol g−1 and 25.7 mmol g−1 at 1 and 20 bar, respectively. More severe activation generates activated carbons with surface area and pore volume of up to 3802 m2 g−1 and 2.98 cm3 g−1, respectively, and which possess significant microporosity combined with mesoporosity resulting in exceptional total hydrogen storage of up to 7.5 wt% at −196 °C and 20 bar, rising to 9.7 wt% and 14.9 wt% at 40 bar and 150 bar, respectively, while at room temperature total uptake reaches 4.4 wt%. The porosity of the CNT superstructures can thus be tailored towards CO2 or hydrogen uptake applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Highlighting materials research in the UK for energy and sustainability

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...