Synthesis of hydrophilic surface ion-imprinted polymer based on graphene oxide for removal of strontium from aqueous solution†
Abstract
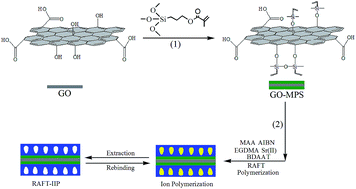
A novel hydrophilic ion-imprinted polymer based on graphene oxide has been synthesized by reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization with surface imprinting technique. Methylacrylic acid is used as a hydrophilic functional monomer. The resultant adsorbent is verified by UV-vis scanning spectrophotometer, Fourier transmission infrared spectrometry, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, X-ray diffraction, water contact angle measurements, and thermogravimetric analysis. The results suggest that the surface imprinted polymer synthesized by RAFT is a homogeneous thin layer. Owing to the intrinsic advantages of controlling/living polymerization and surface imprinting technology, the obtained RAFT surface ion-imprinted polymer (RAFT-IIP) exhibits excellent imprinting efficiency and adsorption capacity in comparison to the ion-imprinted polymer prepared by traditional radical polymerization. Furthermore, the adsorption isotherm and recognizing ability towards Sr(II) onto RAFT-IIP and non-imprinted polymer (NIP) are compared in batch experiments. The equilibrium data are well fitted by Langmuir model and RAFT-IIP has higher selectivity and nearly four times larger Langmuir calculated maximum adsorption capacity (145.77 mg g−1) than that of NIP at 25 °C. Meanwhile, RAFT-IIP is regenerated and found to be suitable for reuse in successive adsorption–desorption cycles five times without significant loss in adsorption capacity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...