Sulfonated graphene oxide–silica for highly selective Nafion-based proton exchange membranes†
Abstract
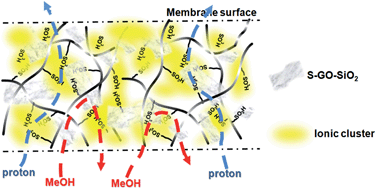
In the current study, sulfonated graphene oxide–silica (S-GO–SiO2) nanohybrid particles were obtained first. The FTIR, TGA, XRD, Raman, AFM, FE-SEM and EDX characterizations were employed to confirm the successful decoration of SiO2 onto GO surface and the attachment of sulfonic acid groups onto the GO–SiO2 surface. Then, S-GO–SiO2/Nafion proton exchange membranes (PEMs) were prepared via solution casting. S-GO–SiO2 had a good dispersibility inside the membrane matrix. The increased water uptake and the incorporated –SO3H groups bestowed a large increase in proton conductivity upon these composite PEMs. Meanwhile, the barrier effect of two-dimensional S-GO–SiO2 contributed to the obvious reduction in methanol permeability of the composite PEMs, as a result of the increased tortuosity of the transport channels. Therefore, novel S-GO–SiO2/Nafion PEMs with enhanced selectivity (the ratio of proton conductivity to methanol permeability) were obtained. Even under harsh conditions, such as high methanol concentration and/or increased temperature, the membrane selectivity of S-GO–SiO2/Nafion composite membranes was still nearly two-orders-of-magnitude higher than that of the recast Nafion membrane. It renders this type of composite PEMs a very promising candidate for the application in DMFC. All the conclusions were demonstrated by various characterizations, such as (FE-) SEM, TEM, AFM, FTIR, TGA, water uptake, etc.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...