Surfactant recovery from mesoporous metal-modified materials (Sn–, Y–, Ce–, Si–MCM-41), by ultrasound assisted ion-exchange extraction and its re-use for a microwave in situ cheap and eco-friendly MCM-41 synthesis
Abstract
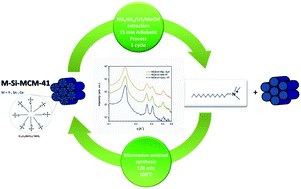
Different metal substituted (Y, Sn and Ce) MCM-41 materials were synthesized and detemplated by a low temperature surfactant removal methodology. All metal substituted materials showed an increase in the d100 lattice parameter compared to the parent MCM-41 matrices. The increase depends on both the metal type and amount that is successfully incorporated by direct conventional hydrothermal synthesis. The metal modified MCM-41 materials were detemplated by an ultrasound assisted (US) ion-exchange process using methanol as the solvent (NH4NO3/US/MeOH). The effect of the ultrasound amplitude, extraction time and salt concentration were explored, and optimal values were determined for Y–MCM-41 detemplation (40 mM of NH4NO3, 60% of US amplitude and 15 min of adiabatic treatment). The removal percentage achieved with these values was in the following order: Y (97.7%) > Ce (94.4%) > Sn (92.1%) > Si (90.3%). Several techniques (SAXS, FTIR, TGA, 1H MAS, 29Si HPDEC MAS NMR and N2 physisorption) demonstrated that the mesoporous materials keep their hexagonal structure and high surface area after the NH4NO3/US/MeOH surfactant extraction. Moreover, the thermal shrinkage of the structure was reduced in the following order: Si (0.6%) < Sn (4%) < Ce (5%) < Y (9%) < calcined samples (from 9 to 15%). The surfactant recovered was successfully recycled in a consecutive microwave assisted hydrothermal synthesis cycle (MW-HT). The synergy of different strategies (MW-HT synthesis, NH4NO3/US/MeOH surfactant removal and surfactant recovery) produces considerable time, energy and cost abatement, environmental impact reduction and promising scale up projections in the eco-friendly synthesis of MCM-41 materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...