Nanostructured SnSb/MOx (M = Al or Mg)/C composites: hybrid mechanochemical synthesis and excellent Li storage performances
Abstract
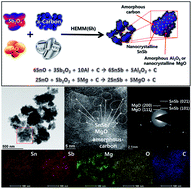
A simple, inexpensive, fast, and scalable method of transforming micron-sized metal oxides into new intermetallic compound nanocomposites by a hybrid mechanochemical synthesis using a high-energy mechanical milling technique was developed. The SnSb/MOx (M = Al or Mg)/C nanocomposites, synthesized by the mechanochemical reduction of SnO and Sb2O3 with Al or Mg, respectively, in the presence of carbon, were confirmed, by using various analytical techniques, to be composed of extremely small SnSb nanocrystallites, amorphous Al2O3 or nanocrystalline MgO, and amorphous carbon. Among the fabricated nanocomposites, the SnSb/MgO/C nanocomposite showed excellent electrochemical properties, such as a high energy density (1st charge: 572 mA h g−1 or ca. 3800 mA h cm−3), cycling durability (above 490 mA h g−1 or ca. 3300 mA h cm−3 over 150 cycles), good initial coulombic efficiency (ca. 81.3%), and a fast rate capability (1C: 480 mA h g−1, 3C: 420 mA h g−1). These excellent electrochemical properties demonstrated by the SnSb-based nanocomposite electrodes confirmed their potential as alternative anode materials for Li-ion batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...