The role of yttrium content in improving electrochemical performance of layered lithium-rich cathode materials for Li-ion batteries
Abstract
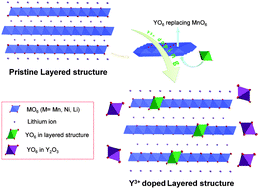
The promising layered lithium-rich cathode materials, Li1.2Mn0.6−xNi0.2YxO2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.05), have been synthesized by substituting Mn4+ in Li1.2Mn0.6Ni0.2O2 with unusually large Y3+ ions, in order to improve their cycling performance and rate capability. An oxalate

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...