Binder-free Co–Mn composite oxide for Li–air battery electrode
Abstract
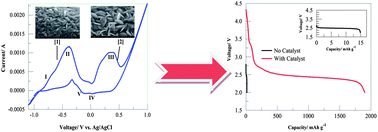
Binder-free Co–Mn composite oxide was successfully deposited at low temperature on a woven substrate through a combination of electroless and electrolytic steps. The principle of the approach was illustrated with cobalt metal and a successful thin film metal oxide formation was supported by CV, XRD and XPS data. The viability of the binder-free Co–Mn oxide electrode was tested as a Li–air battery electrocatalyst and yielded an initial specific capacity of up to 2000 mA h g−1 and survived multiple charge–discharge–recharge cycles. The oxidation time in the electrolytic oxidation-step was found to affect the battery discharge period. In comparison to the conventional polymeric binder methods, the present binder-free method is potentially adaptable to a roll–roll continuous processing approach.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...