Taking advantage of a terpyridine ligand for the deposition of Pd nanoparticles onto a magnetic material for selective hydrogenation reactions†
Abstract
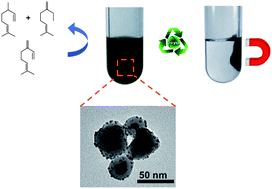
A hybrid terpyridine ligand was designed to functionalize a magnetic support constituted of magnetite cores surrounded by a silica shell with the aim of improving the stabilization of supported-palladium nanoparticles for the later application of the obtained composite nanomaterial in hydrogenation catalysis. The preparation of the nanomaterial was performed by direct decomposition of the organometallic complex [Pd2(dba)3] on the terpyridine-modified magnetic support providing well-dispersed Pd NPs of 2.5 ± 0.6 nm mean size. This new nanomaterial is a highly active catalyst for the hydrogenation of cyclohexene under mild conditions reaching turnover frequencies up to ca. 58 000 h−1 or 129 000 h−1 when corrected for surface Pd atoms. Furthermore, in the hydrogenation of β-myrcene, this nanocatalyst is highly selective for the formation of monohydrogenated compounds. When compared to a similar nanocatalyst consisting of palladium nanoparticles supported on an amino-modified magnetic support or on Pd/C, the activity and selectivity of the nanocatalyst are largely increased. These results show how the design of an appropriate hybrid ligand used to functionalize the support can strongly influence the catalytic properties of supported metal nanoparticles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...