Tuning mass transport in magnetic nanoparticle-filled viscoelastic hydrogels using low-frequency rotating magnetic fields†
Abstract
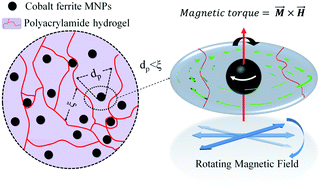
This study investigates the response of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), dispersed in a viscoelastic hydrogel, to an external rotating magnetic field (RMF) for the purpose of developing a new class of magneto-responsive materials with tunable mass transport properties. Ferrogels were prepared by chemical cross-linking and polymerization of acrylamide in colloidal dispersions of thermally blocked MNPs of cobalt ferrite. Magnetization measurements of ferrogels in a swollen state revealed a transitional state from ferromagnetism to superparamagnetism through the shrinkage of hysteresis loops and the reduction of remanent magnetization. A quantitative analysis of magnetization data indicated the existence of hydrodynamically free MNPs, susceptible to Brownian relaxation along with the blocked ones. It was found through rheological analysis that inclusion of MNPs within the polymer matrix significantly alters the ferrogel's elasticity. At low chemical crosslinking ratios, MNPs improve elasticity through the formation of physical crosslinks ensued by reduction in the fraction of the free MNPs. As the crosslinking ratio was increased, the polymer network showed a tendency toward blockage of more MNPs. Effective diffusion coefficients in both particle-free hydrogels and ferrogels were obtained by measuring the release kinetics of a model compound in the absence and presence of an external low-frequency RMF. Experimental results showed that conversion of magnetic energy to kinetic energy by rotational movement of the free MNPs in a RMF escalates mass transport provided that hydrodynamically free MNPs are available within the ferrogels. The effectiveness of excitation by a RMF showed correlation with the density of free MNPs. Release experiments at constant RMF intensity and various frequencies revealed augmentation of effective diffusivities as the frequency was increased from 10 to 75 Hz.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...