Depletion and double layer forces acting between charged particles in solutions of like-charged polyelectrolytes and monovalent salts
Abstract
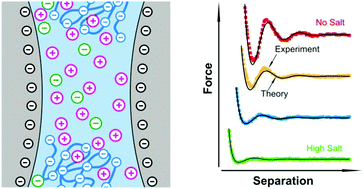
Interaction forces between silica particles were measured in aqueous solutions of the sodium salt of poly(styrene sulphonate) (PSS) and NaCl using the colloidal probe technique based on an atomic force microscope (AFM). The observed forces can be rationalized through a superposition of damped oscillatory forces and double layer forces quantitatively. The double layer forces are modeled using Poisson–Boltzmann (PB) theory for a mixture of a monovalent symmetric electrolyte and a highly asymmetric electrolyte, whereby the multivalent coions represent the polyelectrolyte chains. The effective charge of the polyelectrolyte is found to be smaller than the bare number of charged groups residing on one polyelectrolyte molecule. This effect can be explained by counterion condensation. The interplay between depletion and double layer forces can be further used to predict the phase of the depletion force oscillations. However, this picture holds only at not too elevated concentrations of the polyelectrolyte and salt. At higher salt concentrations, attractive van der Waals forces become important, while at higher polyelectrolyte concentrations, the macromolecules adsorb onto the like-charged silica interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...