Heteropoly acids triggered self-assembly of cationic peptides into photo- and electro-chromic gels†
Abstract
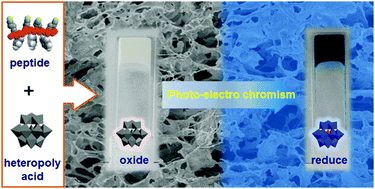
A series of cationic peptides with alternating lysines and hydrophobic residues were designed and synthesized. These kinds of short peptides with protonated lysines can complex with anionic heteropoly acids (HPAs) to form a stable gel in water/ethanol mixed solution. Circular dichroism spectroscopy showed that the short peptides adopted a mixed conformation (β-sheet and random-coil) within the gel matrix. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy revealed that the heteropoly acids, acting as nanosized cross-linkers, first initiated the self-assembly of the cationic peptides into spherical nanostructures. Then these nanospheres accumulated with each other through hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions to form large sheet-like assemblies, which further interconnected with each other forming continuous 3D network structures. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy showed that the structural integrity of the HPAs was maintained during the gelation process. The resultant hybrid gels showed reversible photo- and elecrtro-chromic properties. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy revealed that the hybrid gels, capable of persistent and reversible changes of their colour, are attributed to the intervalence charge-transfer transition of the HPAs. Reversible information writing and erasing were demonstrated through a repeated photo-lithograph or electric stimuli without significant loss of the gel performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...