Water fluxes and encapsulation efficiency in double emulsions: impact of emulsification and osmotic pressure unbalance†
Abstract
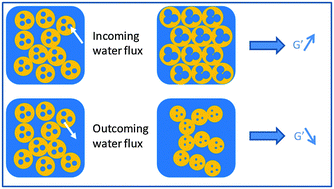
We study the influence of the emulsification process on encapsulation efficiency of drugs in double water-in-oil-in-water emulsions. Two drugs were used, first vitamin B12 which can be considered as a model drug and secondly a suspension of Cydia pomonella Granulovirus (CpGV), a virus used in organic agriculture to protect fruits against the Carpocapse insect. Encapsulation is measured by classical UV-Vis spectroscopy method. Additionally we show that rheology is a useful tool to determine water exchanges during emulsification. In a two-step emulsification process, using rotor-stator mixers, encapsulation reaches high levels, close to 100% whatever the flowing regime. This encapsulation decreases only if two conditions are fulfilled simultaneously: (i) during the second emulsification step the flow is turbulent and (ii) it leads to excessive fragmentation inducing formation of too small drops. We also investigate the effect of a deliberate loss of osmotic pressure balance on the encapsulation and characterize the induced water fluxes. We show that encapsulation of vitamin B12 is not affected by the osmotic pressure unbalance, while water exchanges, if they exist, are very fast and aim at restoring equilibrium. As a consequence, the emulsification efficiency is not very sensitive to osmotic stresses provided that the interfaces resist mechanically.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...